C++多态
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Wood{
protected:
int height;
int cost;
public:
Wood(int height,int cost)
{
this->height=height;
this->cost=cost;
}
virtual void show()
{
cout<<height<<endl;
}
};
class Table:public Wood{
public:
Table(int height,int cost): Wood(height,cost){}
void show()
{
cout<<"Table:"<<height<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Table t1(55,61);
Wood *ptr=&t1;
ptr->show(); // Table:55
return 0;
}
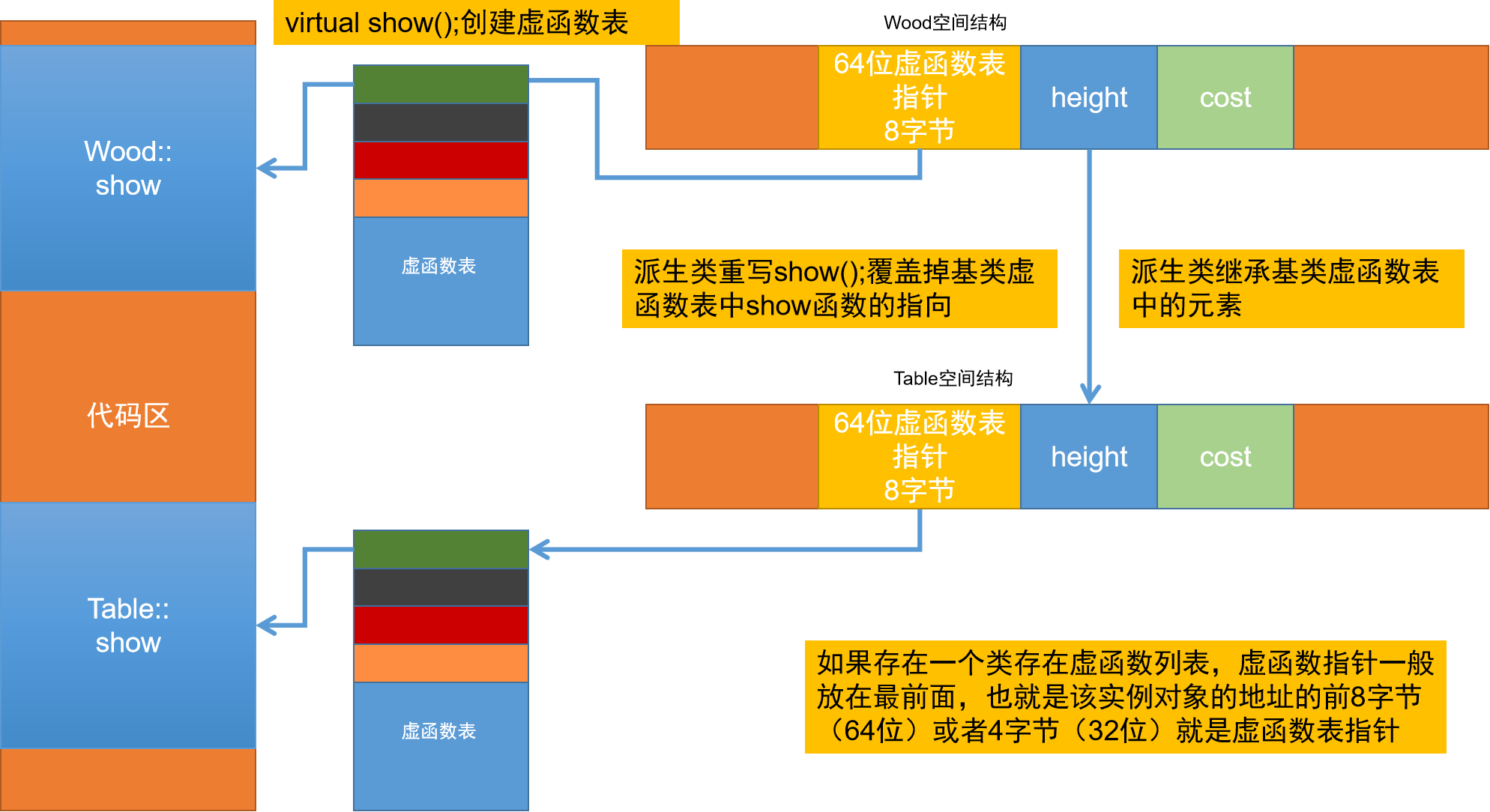
- 当类中出现了虚函数,该类中就会生成一个虚函数指针,该虚函数指针指向虚函数表,虚函数表实质上来说是一个数组
- 当基类中有虚函数时,派生类中也会生成一个虚函数指针,指向虚函数表,这个表继承了基类虚函数表的元素
- 如果重写虚函数就会修改虚函数表的内容,让其指向自己的函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Wood{
public:
Wood(int height,int cost)
{
this->height=height;
this->cost=cost;
}
virtual void show()
{
// cout<<height<<endl;
cout<<"hell"<<endl;
}
protected:
int height;
int cost;
};
class Table:public Wood{
public:
Table(int height,int cost): Wood(height,cost){}
void show()
{
cout<<"Table:"<<height<<endl;
}
};
typedef void (*Myfunc)();
int main()
{
Wood w1(12,36);
Table t1(55,61);
long long *wptr=(long long *)(((long long *)(*((long long *)&w1)))[0]);
long long *tptr=(long long *)(((long long *)(*((long long *)&t1)))[0]);
Myfunc ptr=(Myfunc)wptr;
ptr(); // hell
cout<<wptr<<endl; //0x402d80
cout<<tptr<<endl; //0x402e40
return 0;
}




